https://doi.org/10.1351/goldbook.08377
Technique in solid-state nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy to remove or reduce the influence of anisotropic interactions by rapid sample rotation about the magic angle, where \(\boldsymbol{B_{0}}\) is external magnetic induction and \(\uptheta\) is the axis of rotation of the sample at an angle of approx. \(\pu{54.74\!^{\circ}}\) to the external magnetic induction.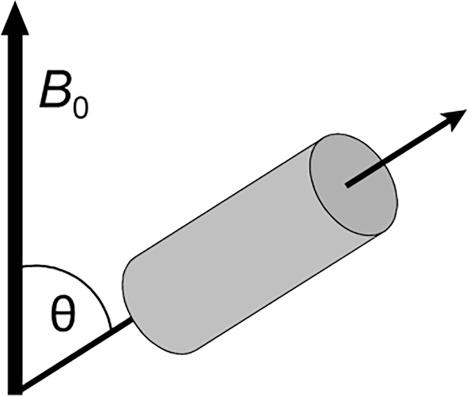
Notes:
- Much like in the case of solutions, MAS effectively averages orientation-dependent interactions and allow high resolution spectra.
- The rate of spinning must be greater than or equal to the magnitude of the anisotropic interaction to average it to zero.

Source:
PAC, 2021, 93, 647. 'Glossary of methods and terms used in analytical spectroscopy (IUPAC Recommendations 2019)' on page 695 (https://doi.org/10.1515/pac-2019-0203)
PAC, 2021, 93, 647. 'Glossary of methods and terms used in analytical spectroscopy (IUPAC Recommendations 2019)' on page 695 (https://doi.org/10.1515/pac-2019-0203)