https://doi.org/10.1351/goldbook.08785
A polymer composed of molecules whose backbone is a sequence of alternating single and multiple bonds: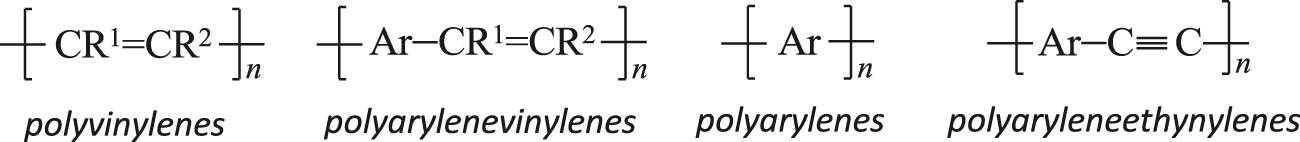 where
where
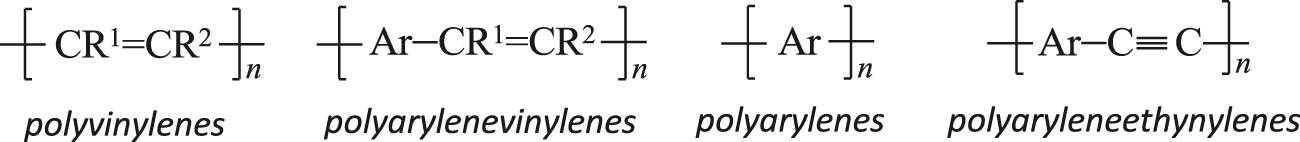
Notes:
- Overlaps of neighboring
- Conjugated polymers are mostly linear or branched polymers. However, they can also have a dendritic, hyperbranched, network, rotaxane or metallo-supramolecular chain architecture.
- Polymers such as polysilanes, polygermanes and polystannanes with significantly occupied LUMO orbitals due to low bandgap energy and thus show the delocalization of electrons sometimes called