https://doi.org/10.1351/goldbook.A00266
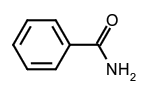
- Derivatives of oxoacids RkE(=O)l(OH)m (l ≠ 0) in which an acidic hydroxy group has been replaced by an amino or substituted amino group. Chalcogen replacement analogues are called thio-, seleno- and telluro-amides. Compounds having one, two or three acyl groups on a given nitrogen are generically included and may be designated as primary, secondary and tertiary amides, respectively, e.g. benzamide,
 N,N-dimethylmethanesulfonamide,
N,N-dimethylmethanesulfonamide,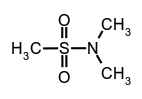 secondary amides (see imides),
secondary amides (see imides),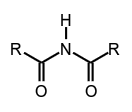 tertiary amides,
tertiary amides,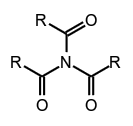 phenylphosphonamidic acid.
phenylphosphonamidic acid.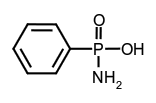 Notes:
Notes:- Amides with NH2, NHR and NR2 groups should not be distinguished by means of the terms primary, secondary and tertiary.
- Derivatives of certain acidic compounds RnE(OH)m, where E is not carbon (e.g. sulfenic acids, RSOH, phosphinous acids, R2POH), having the structure RnE(NR2)m may be named as amides but do not belong to the class amides proper, e.g. CH3CH2SNH2 ethanesulfenamide or ethylsulfanylamine.
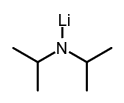
- The term applies also to metal derivatives of ammonia and amines, in which a cation replaces a hydrogen atom on nitrogen. Such compounds are also called azanides, e.g. lithium diisopropylamide, synonym lithium diisopropylazanide.