https://doi.org/10.1351/goldbook.C00948
When in a chain reaction there is a net increase in the number of chain carriers there is said to be chain branching. A simple example of a chain-propagating reaction leading to chain branching is: 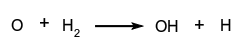 in which there is one chain carriers (an oxygen atom) on the left and two chain carriers (a hydrogen atom and a hydroxyl radical) on the right.
in which there is one chain carriers (an oxygen atom) on the left and two chain carriers (a hydrogen atom and a hydroxyl radical) on the right.
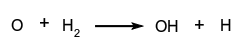
See also: degenerate chain branching