https://doi.org/10.1351/goldbook.I03183
The generation of one or more ions. It may occur, e.g. by loss of an electron from a neutral molecular entity, by the unimolecular heterolysis of such an entity into two or more ions, or by a heterolytic substitution reaction involving neutral molecules, such as: 
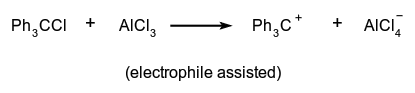
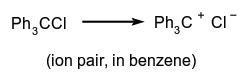 The loss of an electron from a singly, doubly, etc. charged cation is called second, third, etc. ionization. This terminology is used especially in mass spectroscopy.
The loss of an electron from a singly, doubly, etc. charged cation is called second, third, etc. ionization. This terminology is used especially in mass spectroscopy.

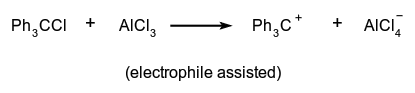
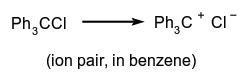
See also: dissociation, ionization energy